Description Active Substances Route of administration Indication: In women testosterone propionate is used to treat vascular and nerve climacteric disorders, when preparations against estrogen (ovarian and breast cancer, uterine bleeding) concomitantly with radiotherapy in breast and ovarian cancer (usually in women aged under 60 years) in dysfunctional uterine bleeding women over 45 years. Contra-indications: Administration: The most optimal dose to administer is 50 mg increased up to 100mg, every day or every other day. The whole each week dosage will be inside range of 300-700mg. Medical action: Precautions: Side effects: Overdosage: In this case the following measures should be taken: gastric lavage, compelled alkalic symptom, restoration associated with liquid, solution and chemical stability, dialysis and also supportive remedy.
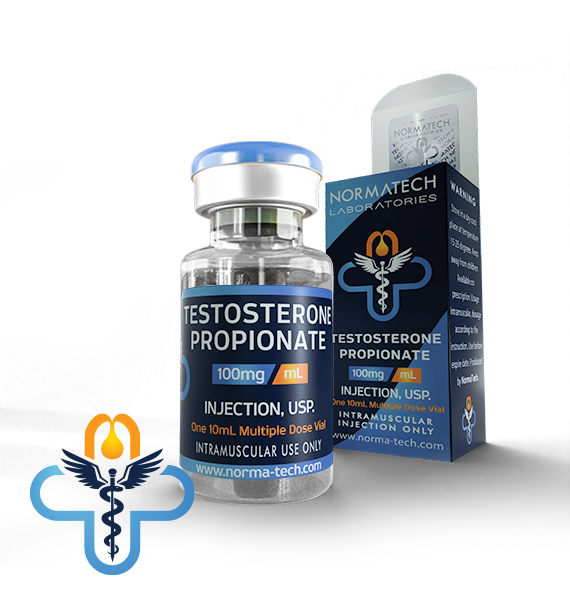
1 vial contains 10 ml solution for injections;
Each ml of SP Propionate contains 100 mg of Testosterone Propionate;
For intramuscular use only;
Testosterone propionate is used in the treatment of androgenic deficit after castrating, eunuchoidism, impotence hormonal origin, signs of male climax (decreased libido and physical and intellectual activity) in acromegaly, in early-stage prostate hypertrophy, osteoporosis caused by androgenic insufficiency.
Persons that have hypersensitivity to testosterone propionate and its components, with the prostate related or perhaps cancer of the breast, prostatic hypertrophy with symptoms of urinary system problems, nephrotic syndrome or even the nephrotic period associated with nephritis, edema, hypercalcemia, hepatic dysfunction, diabetes mellitus, and coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction with inside anamnesis, atherosclerosis in older males, being pregnant, breastfeeding are not indicated to use testosterone propionate.
SP Propionate can be administered only by intramuscular injection, into the gluteal muscle. The dosage cycle is actually changed individually depending on the disease, intercourse, grow older, clinical result.
Testosterone is the main androgen hormone produced by the testicles. Testosterone is responsible for development of men sexual intercourse organs and also extra sex qualities (readiness regarding prostate related, seminal vesicles, penis as well as scrotum), man head of curly tresses distribution (encounter, pubic bone, upper body) building laryngeal muscle tissue and the body extra weight syndication. It keeps the balance of sodium, blood potassium and phosphorus, increases protein constructive metabolism and reduce catabolism. It increases plasma concentrations, in the prepubertal period it causes stunted progress as well as epiphyseal closure. Testosterone propionate provides the production of glycoprotein and also erythrocytes.
Persons that suffer from latent or overt cardiac, impaired renal function, hypertension, epilepsy or migraine (or a history of the presence of these conditions) must be constantly monitored because testosterone may cause sodium and water retention. During the cure period, the liver functions should be monitored. In patients with breast cancer, hypernephroma, lung cancer bone metastases will be controlled the level of calcium in blood and urine. Testosterone administration in prepubertal adolescents should be given with caution to avoid premature cessation of growth and puberty.
• Abnormalities of the prostate;
• Women – bleeding from the genital tracts, increased libido, prolonged administration of virilization symptoms are possible;
• Hirsutism, gynecomastia;
• Seborrhea, acne, oily skin, hair loss;
• Sodium and water retention, edema;
• Symptoms of hypercalcemia;
• Priapism and other symptoms of sexual hyperstimulation (frequent erection);
• Prepubertal age teenagers – accelerate sexual development, increased frequency of erections, increased sexual organ size, premature closure of the epiphyseal
• impaired spermatogenesis and sperm maturation disorder, oligospermia and reduced volume of ejaculate;
• Thrombophlebitis;
• Nausea, cholestatic jaundice, increased liver transaminase levels (normalized to discontinuation);
• Headache, depression, aggression, anxiety, sleep disorders, numbness.
Possible pain, itching and redness at the injection site.
If testosterone propionate is administered in high doses for a long period then it is the risk to develop pathology. If an overdose takes place then the administration should be discontinued and right away the symptoms disappear the treatment can be continued with lower doses.
Testosterone Propionate
Testosterone propionate is used in the treatment of androgenic deficit after castrating, eunuchoidism, impotence hormonal origin, signs of male climax (decreased libido and physical and intellectual activity) in acromegaly, in early-stage prostate hypertrophy, osteoporosis caused by androgenic insufficiency.
Category: Injection Preparations
Loading...